请求合并
你可以在HystrixCommand之前放置一个请求合并器(HystrixCollapser为请求合并器的抽象父类),该合并器可以将多个发往同一个后端依赖服务的请求合并成一个。
下图展示了在两种场景下(未增加请求合并器和增加请求合并器),线程和网络连接数量(假设所有请求在很小的时间窗口,例如10ms,是并发的):
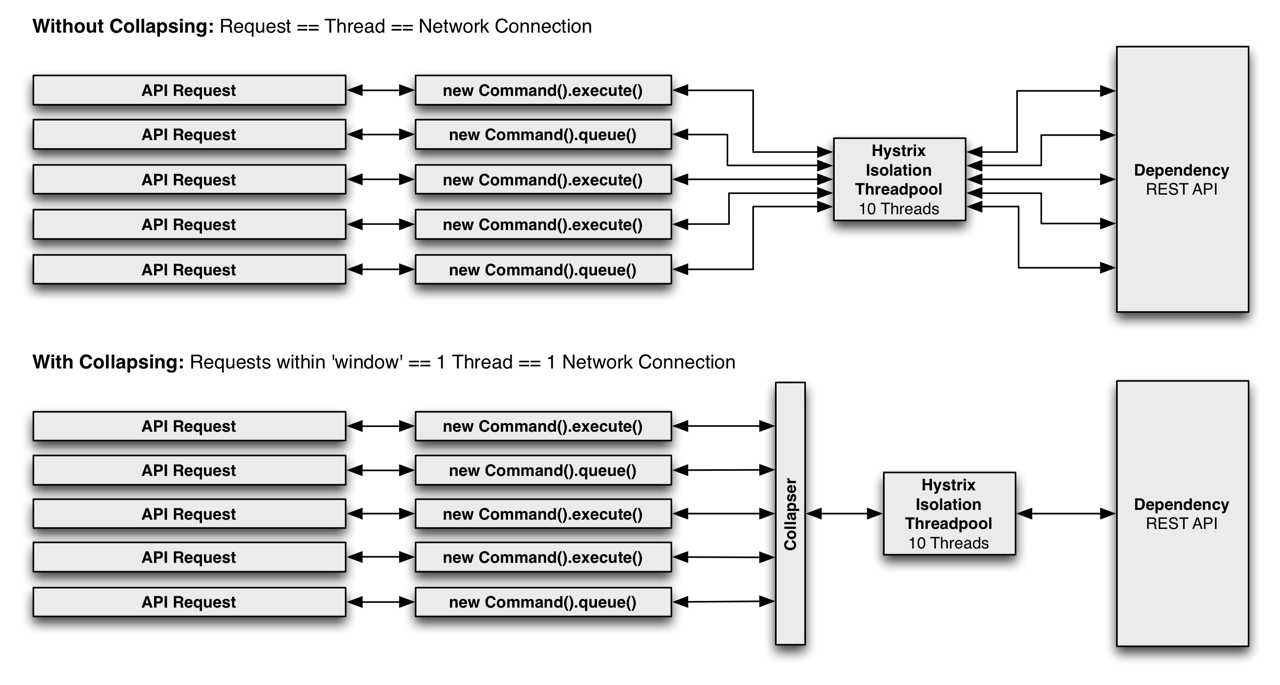
为什么要使用请求合并
在并发执行HystrixCommand时,利用请求合并能减少线程和网络连接数量。通过使用HystrixCollapser,Hystrix能自动完成请求的合并,开发者不需要对现有代码做批量化的开发。
全局上下文(适用于所有Tomcat线程)
理想情况下,合并过程应该发生在系统全局层面,这样用户发起的,由Tomcat线程执行的所有请求都能被执行合并操作。
例如,有这样一个需求,用户需要获取电影评级,而这些数据需要系统请求依赖服务来获取,对依赖服务的请求使用HystrixCommand进行包装,并增加了请求合并的配置,这样,当同一个JVM中其他线程需要执行同样的请求时,Hystrix会将这个请求同其他同样的请求合并,只产生一个网络请求。
注意,合并器会传递一个HystrixRequestContext对象到合并的网络请求中,因此,下游系统需要支持批量化,以使请求合并发挥其高效的特点。
用户请求上下文(适用于单个Tomcat线程)
如果给HystrixCommand只配置成针对单个用户请求合并,则Hystrix只会在单个Tomcat线程(即请求)中进行请求合并。
例如,如果用户想加载300个视频对象的书签,请求合并后,Hystrix会将原本需要发起的300个网络请求合并到一个。
对象模型和代码复杂度
很多时候,当你创建一个对象模型,适用于对象的消费者逻辑,结果发现这个模型会导致生产者无法充分利用其拥有的资源。
例如,这里有一个包含300个视频对象的列表,需要遍历这个列表,并对每个对象调用getSomeAttribute()方法,这是一个显而易见的对象模型,但如果简单处理的话,可能会导致300次的网络请求(假设getSomeAttribute()方法内需要发出网络请求),每一个网络请求可能都会花上几毫秒(显然,这样方式非常容易拖慢系统)。
当然,你也可以要求用户在调用getSomeAttribute()之前,先判断一下哪些视频对象真正需要请求其属性。
或者,你可以将对象模型进行拆分,从一个地方获取视频列表,然后从另一个地方获取视频的属性。
但这些实现会导致API非常丑陋,且实现的对象模型无法满足用户使用模式。并且在企业级开发时,很容易因为开发者的疏忽导致错误或者不够高效,因为不同的开发者可能有不同的请求方式,这样一个地方的优化不足以保证在所有地方都会有优化。
通过将合并逻辑下沉到Hystrix层,不管你如何设计对象模型,或者以何种方式去调用依赖服务,又或者开发者是否意识到这些逻辑需不需要优化,这些都不需要考虑,因为Hystrix能统一处理。
getSomeAttribute()方法能放在它最适合的位置,并且能以最适合的方式被调用,Hystrix的请求合并器会自动将请求合并到合并时间窗口内。
请求合并带来的额外开销
请求合并会导致依赖服务的请求延迟增高(该延迟为等待请求的延迟),延迟的最大值为合并时间窗口大小。
若某个请求耗时的中位数是5ms,合并时间窗口为10ms,那么在最坏情况下(注:合并时间窗口开启时发起请求),请求需要消耗15ms才能完成。通常情况下,请求不太可能恰好在合并时间窗口开启时发起,因此,请求合并带来的额外开销应该是合并时间窗口一个半,在此例中是5ms。
请求合并带来的额外开销是否值得,取决于将要执行的命令,高延迟的命令相比较而言不会有太大的影响。同时,缓存Key的选择也决定了在一个合并时间窗口内能并发执行的命令数量:如果一个合并时间窗口内只有1-2个请求,将请求合并显然不是明智的选择。事实上,如果单线程循环调用同一个依赖服务的情况下,如果将请求合并,会导致整个循环成为系统性能的瓶颈,因为每一个请求都需要等待10ms的合并时间周期。
然而,如果一个命令具有高并发度,并且能批量处理多个,甚至上百个的话,请求合并带来的性能开销会因为吞吐量的极大提升而基本可以忽略,因为Hystrix会减少这些请求所需的线程和网络连接数量。
请求合并器的执行流程
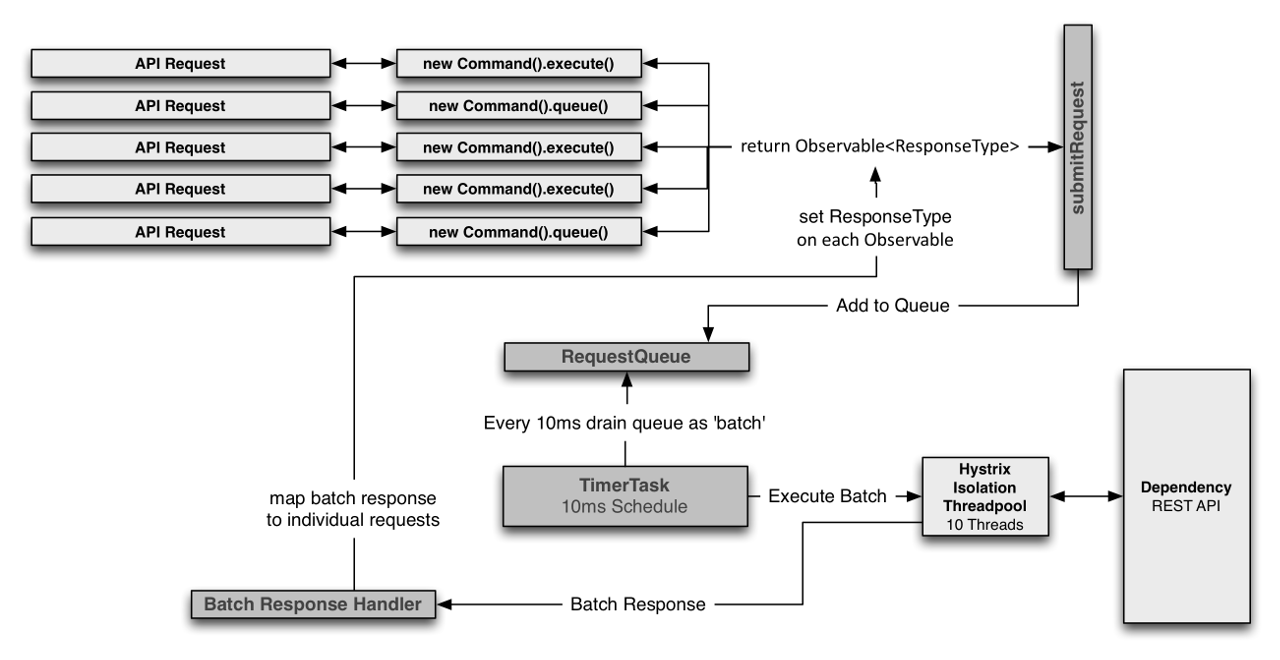
- 提交单个命令请求到请求队列(
RequestQueue) - 定时任务(
TimerTask)固定周期从请求队列获取多个命令执行,合并执行。
HystrixCollapser
com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCollapser是命令合并器抽象父类。
com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixObservableCollapser,另一种命令合并器抽象父类,本文暂不解析。
查看它的属性:
1 | private final RequestCollapserFactory<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> collapserFactory; |
- BatchReturnType泛型,多个命令合并执行返回结果类型
- ResponseType泛型,单个命令执行返回结果类型
- RequestArgumentType泛型,单个命令参数类型
- collapserFactory属性,RequestCollapser工厂,在RequestCollapserFactory详细解析。
- requestCache属性
collapserInstanceWrapper属性,命令合并器包装器。
HystrixCollapserBridge接口为RequestBatch透明调用HystrixCollapser或HystrixObservableCollapser的方法不同的实现
metrics属性
执行命令方式
在Hystrix(二)——命令执行方式中,我们已经看到HystrixCommand提供的四种执行命令方式
HystrixCollapser类似于HystrixCommand,也提供了四种相同的执行命令方式,其中如下三种方式代码基本相同,我们就不重复啰嗦了:
- observe()
- queue()
- execute()
下面一起来看看toObservable()方法的实现。
1 | public Observable<ResponseType> toObservable() { |
- 获取缓存开关和缓存KEY
- 尝试从缓存中获取,如果缓存命中则直接返回缓存中保存的Observable
- 调用
RequestCollapserFactory.getRequestCollapser获取RequestCollapser - 提交单个命令请求到请求队列(RequestQueue),即命令合并执行整体流程第一步
- 如果缓存开启且缓存KEY不为null,将命令请求的Observable保存到缓存中,然后返回缓存Observable;否则返回非缓存Observable
核心方法
getRequestArgument
获得单个命令参数
1 | protected abstract HystrixCommand<BatchReturnType> createCommand(Collection<CollapsedRequest<ResponseType, RequestArgumentType>> requests); |
createCommand
将多个命令请求合并,创建一个HystrixCommand
1 | protected abstract HystrixCommand<BatchReturnType> createCommand(Collection<CollapsedRequest<ResponseType, RequestArgumentType>> requests); |
mapResponseToRequests
将一个HystrixCommand的执行结果,映射回对应的命令请求们
1 | protected abstract void mapResponseToRequests(BatchReturnType batchResponse, Collection<CollapsedRequest<ResponseType, RequestArgumentType>> requests); |
shardRequests
将多个命令请求分片成N个”多个命令请求”。默认实现下,不进行分片
1 | protected Collection<Collection<CollapsedRequest<ResponseType, RequestArgumentType>>> shardRequests(Collection<CollapsedRequest<ResponseType, RequestArgumentType>> requests) { |
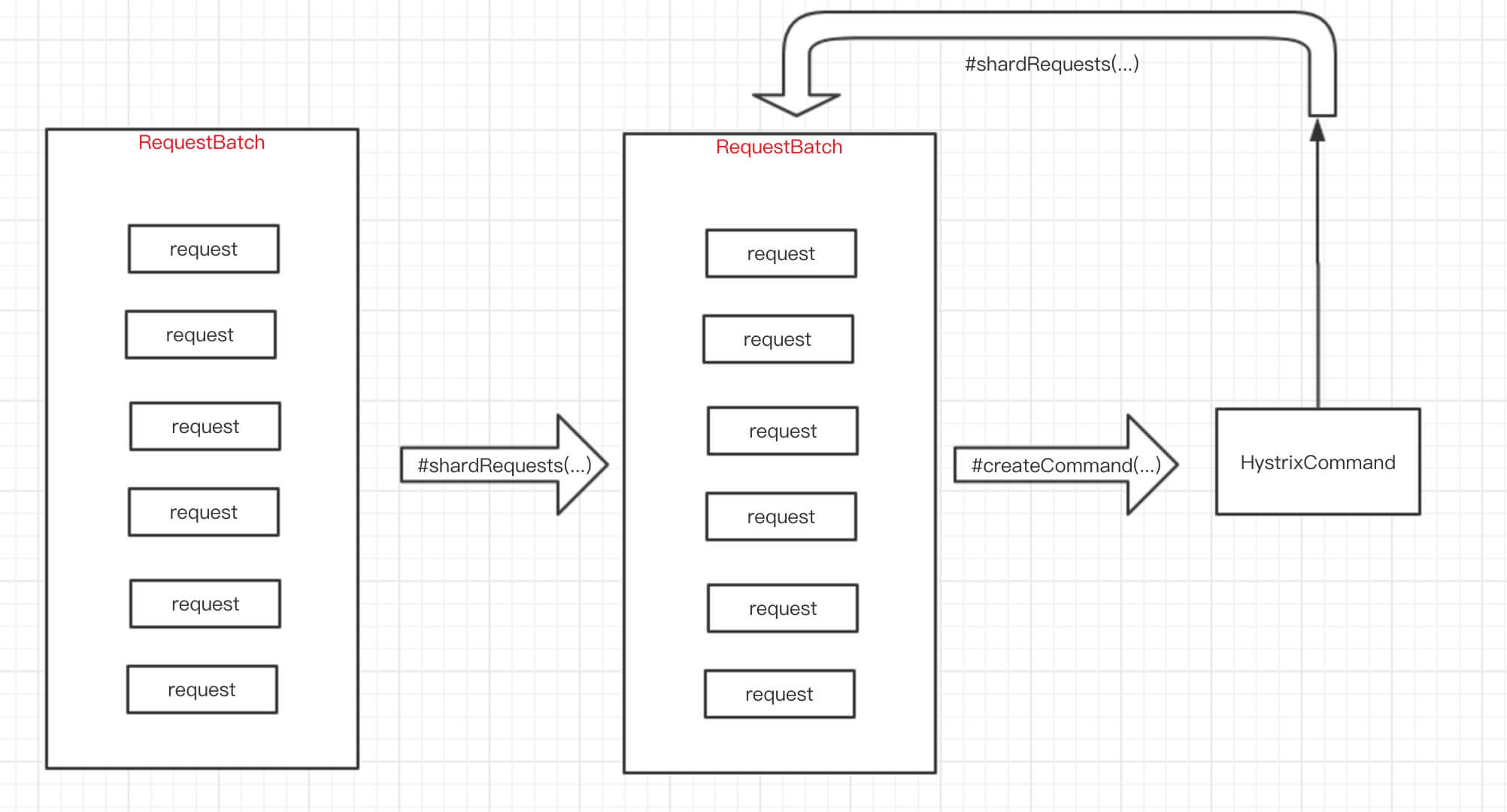
在未重写shardRequests的情况下,整体方法流程如下:
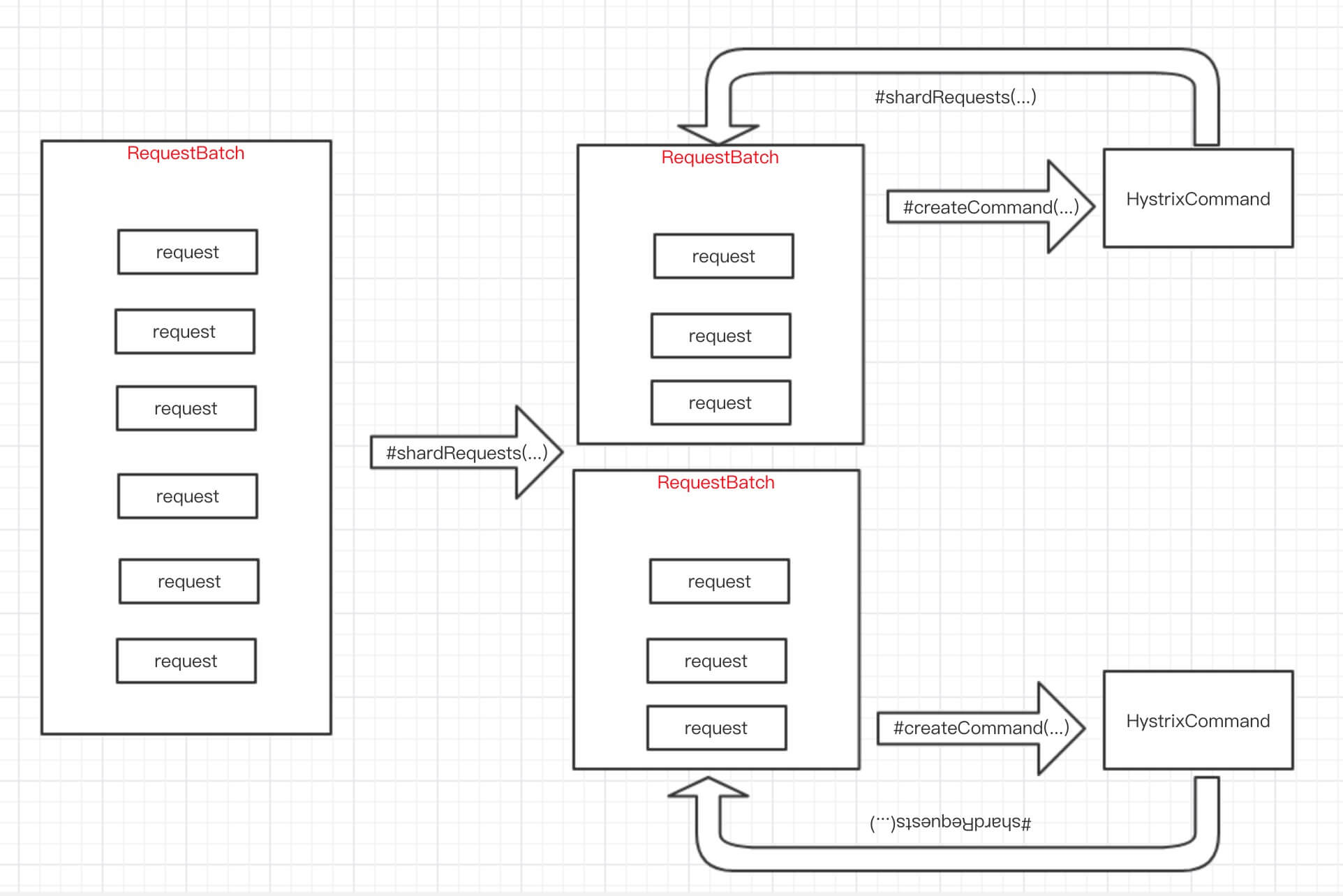
在重写shardRequests的情况下,整体方法流程如下:
RequestCollapserFactory
com.netflix.hystrix.collapser.RequestCollapserFactory是RequestCollapser工厂
1 | public class RequestCollapserFactory<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> { |
timer属性,命令合并器的定时器collapserKey属性,命令合并器标识properties属性,命令合并器属性配置concurrencyStrategy属性,并发策略scope属性,命令请求作用域。目前有两种作用域:
- REQUEST。请求上下文
- GLOBAL。全局
getRequestCollapser()方法获得RequestCollapser。代码如下:
1 | public RequestCollapser<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> getRequestCollapser(HystrixCollapserBridge<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> commandCollapser) { |
根据scope不同,调用两个不同方法,获得RequestCollapser。
getCollapserForUserRequest
1 | private RequestCollapser<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> getCollapserForUserRequest(HystrixCollapserBridge<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> commandCollapser) { |
getCollapserForGlobalScope
1 | private RequestCollapser<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> getCollapserForGlobalScope(HystrixCollapserBridge<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> commandCollapser) { |
RequestCollapser
com.netflix.hystrix.collapser.RequestCollapser是命令请求合并器。主要用于:
- 提交单个命令请求到请求队列(RequestQueue)
- 接收来自定时任务提交的多个命令,合并执行
RequestCollapser构造方法如下:
1 | public class RequestCollapser<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> { |
commandCollapser属性,命令合并器包装器batch属性,RequestBatch,即本文说的请求队列timerListenerReference属性,注册在命令合并器的定时器的监听器。每个RequestCollapser独有一个监听器。该监听器(实际上会使用该监听器创建定时任务)固定周期从请求队列获取多个命令执行,提交RequestCollapser合并执行timerListenerRegistered属性,表示timerListenerReference是否已经注册timer属性,命令合并器属性配置properties属性,命令合并器属性配置concurrencyStrategy属性,并发策略
RequestBatch
com.netflix.hystrix.collapser.RequestBatch是命令请求队列。提供如下功能:
- 命令请求的添加
- 命令请求的移除
- 命令请求的批量执行
RequestBatch构造方法如下:
1 | public class RequestBatch<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> { |
commandCollapser属性,命令合并器包装器maxBatchSize属性,队列最大长度batchStarted属性,执行是否开始argumentMap属性,命令请求参数映射(队列)properties属性,命令合并器属性配置batchLock属性,argumentMap操作的读写锁
submitRequest(arg)
在toObservable()方法里,调用submitRequest(arg)方法,提交单个命令请求到RequestBatch。
1 | public Observable<ResponseType> submitRequest(final RequestArgumentType arg) { |
- 当RequestCollapser的监听任务(CollapsedTask)还未创建,进行初始化
死循环,直到提交单个命令请求到RequestBatch成功
- 获得RequestBatch。从目前代码来看,除非RequestCollapser被
shutdown()后才会出现为null的情况 - 调用
RequestBatch.offer方法,提交单个命令请求到RequestBatch,并获得Observable。这里对arg == null做了特殊处理,因为RequestBatch.argumentMap是ConcurrentHashMap,不允许值为null。 - 添加成功,返回Observable
- 添加失败,执行当前RequestBatch的多个命令合并执行,并创建新的RequestBatch
- 获得RequestBatch。从目前代码来看,除非RequestCollapser被
RequestBatch.offer
RequestBatch.offer方法提交单个命令请求到RequestBatch,代码如下:
1 | public Observable<ResponseType> offer(RequestArgumentType arg) { |
- 获取
batchStarted,检查是否已经开始执行。如果已经开始执行,则添加失败。在RequestBatch.executeBatchIfNotAlreadyStarted方法的开头,优先使用CAS将batchStarted设置为true - 获得读锁
double-check,如果执行已经开始,则添加失败。在RequestBatch.executeBatchIfNotAlreadyStarted方法的开头,优先使用CAS将batchStarted设置为true,再获取写锁,所以会出现该情况。- 超过队列最大长度,则添加失败
创建
com.netflix.hystrix.collapser.CollapsedRequestSubject,并将它添加到队列(argumentMap)CollapsedRequestSubject实现
com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCollapser.CollapsedRequest接口,定义了批量命令执行的请求,不仅限于获得请求参数(getArgument()方法),也包括对批量命令执行结束后,每个请求的结果设置(setResponse、emitResponse、setException、setComplete方法)返回Observable
- 当
argumentMap已经存在arg对应的Observable时,必须开启缓存(HystrixCollapserProperties.requestCachingEnabled = true)功能。原因是,如果存在相同的arg,并且未开启缓存,且执行的是collapsedRequest.toObservable,那么相同的arg将有多个Observable执行命令,此时HystrixCollapserBridge.mapResponseToRequests方法无法将执行结果(Response)赋值到arg对应的命令请求(CollapsedRequestSubject) - 回头看
HystrixCollapser.toObservable方法,也有缓存的功能,是不是重复了呢?argumentMap针对的是ReuqestBatch级的缓存,HystrixCollapser:RequestCollapser:RequestBatch是1:1:N的关系,通过HystrixCollapser.toObservable对缓存的处理逻辑,保证RequestBatch切换后,依然有缓存
- 当
CollapsedRequestSubject
CollapsedRequestSubject的构造方法如下:
1 | class CollapsedRequestSubject<T, R> implements CollapsedRequest<T, R> { |
argument属性,单个命令请求参数valueSet属性,结果(Response)是否设置,通过setResponse/emitResponse方法设置subject属性,可回放执行结果的Subject。此处使用ReplaySubject的主要目的,当HystrixCollapser开启缓存功能时,通过回放执行结果。在HystrixCachedObservable也有相同的实现。另外,这里有一点要注意下,ReplaySubject并没有向任何Observable订阅结果,而是通过setResponse/emitResponse方法这是结果outstandingSubscriptions属性,订阅数量subjectWithAccounting属性,带订阅数量的ReplaySubject。调用RequestBatch.remove方法,移除单个命令请求
RequestBatch.remove
1 | void remove(RequestArgumentType arg) { |
当RequestBatch开始执行,不允许移除单个命令请求
createNewBatchAndExecutePreviousIfNeeded
1 | private void createNewBatchAndExecutePreviousIfNeeded(RequestBatch<BatchReturnType, ResponseType, RequestArgumentType> previousBatch) { |
- 通过CAS修改
batch,保证并发情况下的线程安全。同时注意,此处也新建了RequestBatch,替换到老的RequestBatch - 使用老的RequestBatch,调用
executeBatchIfNotAlreadyStarted方法,命令合并执行
1 | public void executeBatchIfNotAlreadyStarted() { |
- 通过CAS修改
batchStarted,保证并发情况下的线程安全 - 获得写锁。等待调用
offer/remove方法的线程执行完成,以保证命令合并执行时,不再有新的请求添加或移除 - 调用
HystrixCollapserBridge.shardRequests方法,将多个命令请求分片成N个多个命令请求。默认实现下,不进行分片 - 循环N个
多个命令请求 - 调用
HystrixCollapserBridge.createObservableCommand方法,将多个命令请求合并,创建一个HystrixCommand。 - 调用
HystrixCollapserBridge.mapResponseToRequests方法,将一个HystrixCommand的执行结果,映射回对应的命令请求们 - 调用
Observable.doError方法,当命令合并执行发生异常时,设置每个CollapsedRequestSubject的执行结果为异常 - 调用
Observable.doOnCompleted方法,当命令合并执行完成时,检查每个CollapsedRequestSubject是否都有返回结果。一般情况下,是用户实现HystrixCollapser.mapResponseToRequests方法存在bug。另外,如果不设置,将导致无结果的单个命令请求无线阻塞。 - 调用
Observable.subscribe方法,触发HystrixCommand执行 - 如果前面的执行有异常,设置每个
CollapsedRequestSubject的执行结果为异常 - 释放写锁
CollapserTimer
com.netflix.hystrix.collapser.CollapserTimer是命令合并器的定时器接口,定义了提交定时监听器,生成定时任务的接口方法
1 | public interface CollapserTimer { |
RealCollapserTimer
com.netflix.hystrix.collapser.RealCollapserTimer,命令合并器的定时器实现类,代码如下:
1 | public class RealCollapserTimer implements CollapserTimer { |
实际上使用的是HystrixTimer提供的单例
CollapsedTask
com.netflix.hystrix.collapser.RequestCollapser.CollapsedTask,定时任务,固定周期(可配,默认HystrixCollapserProperties.timerDelayInMilliseconds = 10ms)轮询其对应的一个RequestCollapser当前RequestBatch。若有命令需要执行,则提交RequestCollapser合并执行。
代码如下:
1 | private class CollapsedTask implements TimerListener { |
可以看到,CollapsedTask会以IntervalTimeInMilliseconds的时间间隔为周期调用tick()方法,tick()方法会调用callableWithContextOfParent.call(),在其中调用createNewBatchAndExecutePreviousIfNeeded来执行命令合并的请求
请求合并的使用
前面我们学习了Hystrix请求合并的原理,现在来看看如何在Hystrix中使用请求合并功能。
首先我们在eureka-client中增加一个获取批量信息的接口:
1 | ("/users") |
简单起见,这个接口仅仅返回了一个里面保存user: {id}的列表。
继承HystrixCollapser实现请求合并
HystrixCollapser的实现类
1 | public class UserCommandCollapser extends HystrixCollapser<List<String>, String, String> { |
UserService批量查询接口
只需要实现批量查询接口,单个查询也是走批量查询
1 |
|
UserBatchCommand批量查询命令
1 | public class UserBatchCommand extends HystrixCommand<List<String>> { |
测试
我们在服务消费者端创建访问接口,来测试合并请求:
1 |
|
- 首先要初始化
HystrixRequestContext - 创建
UserCommandCollapser类的实例来发起请求,先发送3个请求,然后睡眠300毫秒,再发起1个请求,这样,前3个请求就会被合并为1个请求,第4个请求因为间隔的时间比较久,所以不会被合并,而是单独创建一个线程去处理。
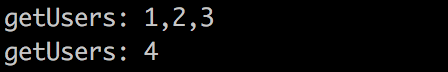
服务提供方的输出结果:
服务消费方的输出结果:
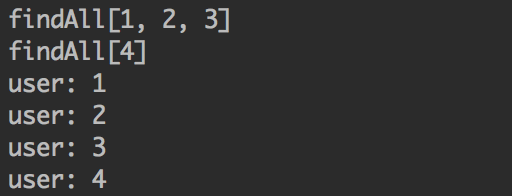
可以看到,前三个请求被合并成一个请求,第四个请求被单独处理
使用注解方式来实现请求合并
上面这种请求合并方式写起来稍微有点麻烦,我们可以使用注解来更优雅地实现这一功能。
首先在UserService中添加两个方法,如下:
1 |
|
在find方法上添加@HystrixCollapser注解实现请求合并。用batchMethod属性指定请求合并后的处理方法,scope属性指定命令合并的范围(REQUEST表示单个请求,GLOBAL表示全局请求),collapserProperties属性指定其他属性。
在UserService写好之后,直接调用就可以:
1 | ("/users") |
和前面一样,前三个请求会进行合并,第四个请求会单独执行。
http://youdang.github.io/2016/02/05/translate-hystrix-wiki-how-it-works/#%E8%AF%B7%E6%B1%82%E5%90%88%E5%B9%B6
https://github.com/YunaiV/Blog/blob/master/Hystrix/2018_11_04_Hystrix%20%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E8%A7%A3%E6%9E%90%20%E2%80%94%E2%80%94%20%E5%91%BD%E4%BB%A4%E5%90%88%E5%B9%B6%E6%89%A7%E8%A1%8C.md
https://blog.csdn.net/u012702547/article/details/78213270
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012256788
https://blog.csdn.net/zhuchuangang/article/details/74663755

