在上一篇文章Spring与MVC(二)中,我们分析了Spring MVC在启动过程中ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet两个类的创建过程。
这篇文章中,我们来分析DispatcherServlet初始化过程,以及DispatcherServlet的处理请求过程。
DispatcherServlet初始化过程
首先看一下DispatcherServlet的继承关系。DispatcherServlet继承自FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet继承自HttpServletBean,HttpServeltBean继承自Java的HttpServlet。
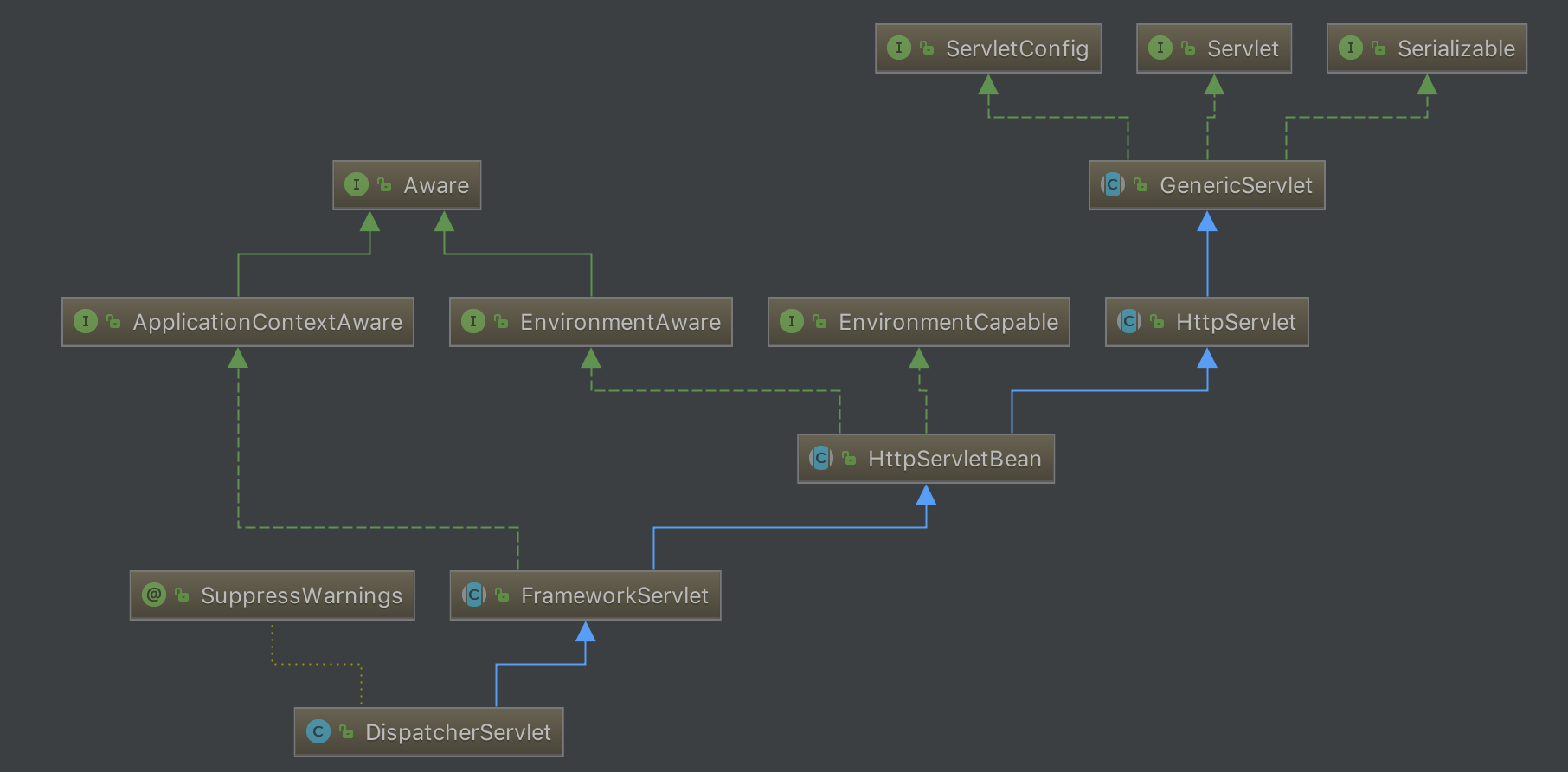
HttpServletBean用于将Servlet中配置的参数设置到相应的属性中。然后调用FrameworkServlet.initServletBean,initServletBean的主要工作是调用initWebApplicationContext()初始化Spring MVC中所使用的WebApplicationContext:
1 | protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { |
首先,从ServletContext中获取WebApplicationContext。
回顾上一篇文章,在创建DispatcherServlet时,使用了我们创建的WebApplicationContext,因此这里的this.webApplicationContext不为空,对其进行各种配置:设置ServletContext、ServletConfig、Namespace、ApplicationListener,最后调用refresh()进行bean的各种初始化。其中,在最后的finishRefresh()方法中,会通过事件的方式通知DispatcherServlet初始化各个策略接口的实现类:
1 | protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { |
DispatcherServlet处理请求过程
HttpServlet提供了service方法用于处理请求,service使用了模板设计模式,在内部对于http get方法会调用doGet方法,http post方法调用doPost方法…
查看FrameworkServlet代码,doGet、doPost等方法调用的是processRequest方法,processRequest方法调用DispatcherServlet.doService执行service的任务,doService委托给doDispatch来做真正的请求分派工作:
1 | protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { |
首先,调用getHandler方法获取HandlerExecutionChain,其中包括了目标方法以及拦截器。然后通过handler获取HandlerAdapter,使用HandlerAdapter调用handler,得到ModelAndView对象。最后调用processDispatchResult方法渲染页面,处理前面调用抛出的异常。

