在我们后端开发中,经常使用redis作为缓存。常见的redis使用场景一般是这样的:使用sorted set存储有序列表,key存储的是数据的id,score作为列表的排序依据;使用字符串存储详细数据的json,key存储的是数据的id。这样我们就可以通过redis获得列表数据的id值,然后使用id去redis中获取数据的详细值。
在这样的使用方式下,每一次的接口请求都需要几十次的redis请求。因为redis占用了连接池资源并且存在固定的网络传输消耗,在读多写少的场景下,大量的redis请求造成的性能损失还是相当可观的。
为了减少的redis访问次数,提升效率,我们需要借助redis的pipeline功能。
pipeline使用
redis本身是基于Request/Response协议的,正常情况下,客户端发送一个命令,等待redis应答,redis在接收到命令,处理后应答。在这种情况下,如果同时需要执行大量的命令,那就需要等待上一条命令应答后再执行,这中间不仅仅多了RTT(Round Time Trip,传播时延(往返)+排队时延(路由器和交换机)+数据处理时延(应用程序)),而且还频繁地调用系统IO,发送网络请求。
pipeline允许客户端可以一次发送多条命令,而不等待上一条命令执行的结果,这和网络的Nagel算法有点像(TCP_NODELAY选项)。不仅减少了RTT,同时也减少了IO调用次数(IO调用涉及到用户态到内核态之间的切换)。
pipeline需要客户端的支持,本文我们以Jedis客户端为例来说明使用pipeline批量获取数据:
1 | // 连接redis |
pipeline性能测试
测试抽象类:
1 | public abstract class AbstractRedis { |
获取数据的普通方式:
1 | public class RedisGet extends AbstractRedis { |
获取数据的pipeline方式:
1 | public class RedisPipelineGet extends AbstractRedis { |
性能测试代码:
1 | public class PerformanceTest { |
性能测试执行结果如下:
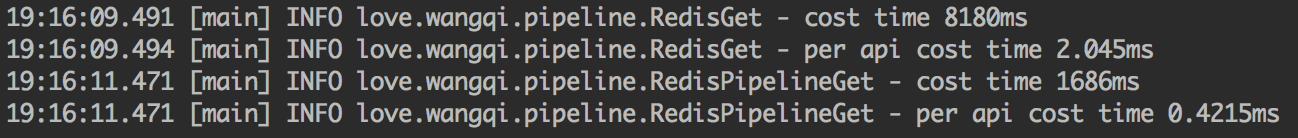
可以看到,每20次的请求,普通方式要比pipeline方式耗费的时间多出4.8倍。pipeline对于qps的提升是非常大的。
pipeline使用的注意点
需要注意的是,pipelined.sync()执行之前不能使用jedis执行普通命令。如果jedis是从Pool中获取的,在pipelined.sync()执行之前不能提早将jedis归还,否则在并发状态下其他线程会取得jedis执行其他命令。
总结
虽然redis是一个性能强大的缓存服务,但是在使用的过程中仍然有性能提示的空间。
https://juejin.im/post/5a31e9f66fb9a0451238f610
https://blog.csdn.net/HG_Harvey/article/details/80082090
https://www.cnblogs.com/jabnih/p/7157921.html
https://www.zhihu.com/question/39244840

